Linux内核编程之等待队列的简单使用
同上一篇《Linux内核编程之完成接口completion的简单使用》,这里对等待队列如何实现也不做深入解释,有兴趣的可以去看Linux源代码,主要在
- include/linux/wait.h
这个头文件里。这里只对如何使用结合demo稍作解释。下面直接给出驱动源代码:
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/moduleparam.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/timer.h> // for timer_list API
#include <linux/param.h> // for HZ
#include <linux/jiffies.h> // for jiffies
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(waitqueue_demo);//定义一个等待队列头
static int waitqueue_flag = 0;//读写flag
static char waitqueue_str[16] = {0x0};
static int waitqueue_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) {
printk("waitqueue opened.\n");
return 0;
}
static int waitqueue_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) {
printk("waitqueue released.\n");
return 0;
}
static ssize_t waitqueue_read(struct file *file, char __user *buffer, size_t count, loff_t *pos) {
ssize_t ret;
printk("waitqueue read.\n");
wait_event_interruptible(waitqueue_demo, waitqueue_flag != 0);//读进程阻塞
ret = copy_to_user(buffer, waitqueue_str, count);
if (ret == 0) {
waitqueue_flag = 0;
return count;
} else {
return -EFAULT;
}
}
static ssize_t waitqueue_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buffer, size_t count, loff_t *pos) {
ssize_t ret;
printk("waitqueue write.\n");
ret = copy_from_user(waitqueue_str, buffer, count);
if (ret == 0) {
waitqueue_flag = 1;
wake_up_interruptible(&waitqueue_demo);//唤醒读进程
return count;
} else {
return -EFAULT;
}
}
static struct file_operations waitqueue_fops =
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = waitqueue_open,
.release = waitqueue_release,
.read = waitqueue_read,
.write = waitqueue_write,
};
static struct miscdevice waitqueue_dev = {
.minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR,
.name = "waitqueue",
.fops = &waitqueue_fops,
};
static int __init waitqueue_demo_init(void)
{
int ret;
printk("init waitqueue demo.\n");
ret = misc_register(&waitqueue_dev);
if (ret) {
printk("misc_register error.\n");
return ret;
}
return 0;
}
static void __exit waitqueue_demo_exit(void)
{
printk("exit waitqueue demo.\n");
misc_deregister(&waitqueue_dev);
}
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("zhuqinggooogle@gmail.com");
module_init(waitqueue_demo_init);
module_exit(waitqueue_demo_exit);
同《Linux内核编程之完成接口completion的简单使用》,这里也是模拟
- 两个进程,一个进程写,另一个进程读。但是,必须保证在一个进程写完后,另一个进程才能读
所以,上层demo基本上不需要修改,只需修改open函数里面的参数,如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
char waitqueue_demo[] = "waitqueue demo";
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int fd = -1;
char buffer[16] = {0x0};
int ret;
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
perror("fork error.\n");
exit(-1);
} else if (0 == pid) {
printf("----child process----\n");
fd = open("/dev/waitqueue", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open error\n");
exit(-1);
}
ret = read(fd, buffer, 16);
if (ret > 0) {
printf("%s\n", buffer);
close(fd);
exit(0);
}
close(fd);
} else if (pid > 0) {
printf("----father process----\n");
fd = open("/dev/waitqueue", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open error\n");
exit(-1);
}
printf("sleep for 10s just for delaying write operation.\n");
sleep(10);
ret = write(fd, waitqueue_demo, sizeof(waitqueue_demo));
if (ret > 0) {
printf("write ok.\n");
close(fd);
exit(0);
}
close(fd);
}
}
编译过程这里就略过了。我们直接把模块插入内核试试:
/mnt/3520d $ insmod waitqueue.ko
init waitqueue demo.
再运行demo看看:
/mnt/3520d $ ./demo
----father procewaitqueue opened.
ss----
sleep fowaitqueue opened.
r 10s just for dwaitqueue read.
elaying write operation.
----child process----
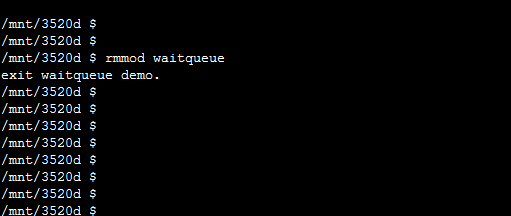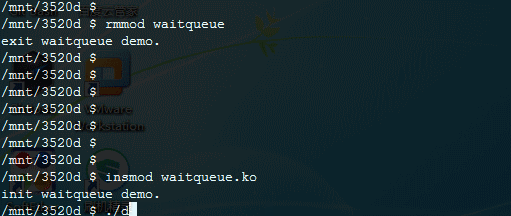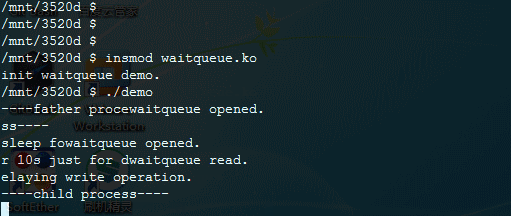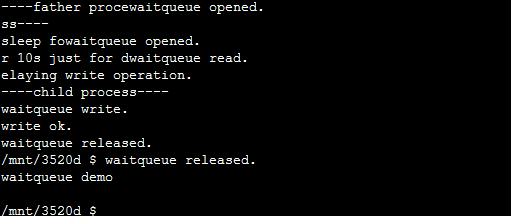
waitqueue write.
write ok.
waitqueue released.
/mnt/3520d $ waitqueue released.
waitqueue demo
打印为什么会错乱就不需要我解释了吧!为了更直观地说明问题,我录制了一个gif图: